Pituitary Adenoma
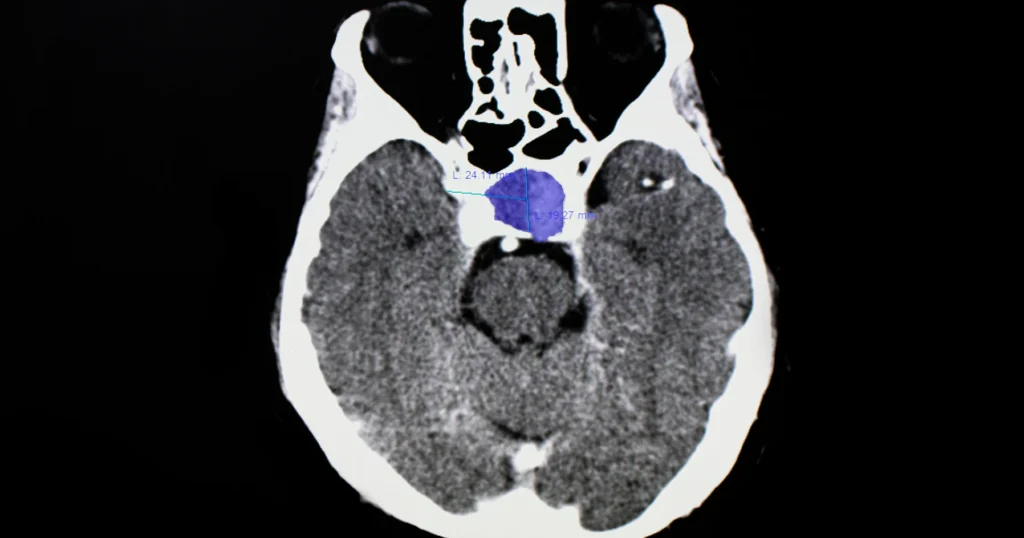
Pituitary Adenoma
Contact Us
Related Videos :
Frequently Asked Questions :
1. What is a pituitary adenoma?
A pituitary adenoma is a benign tumor that originates in the pituitary gland, potentially affecting hormone production and surrounding structures.
2. Are pituitary adenomas cancerous?
No, pituitary adenomas are typically benign (non-cancerous) but can still cause significant health issues.
3. What are the treatment options available?
Treatment options include observation, medications, surgery, and radiation therapy, depending on the tumor’s type and size.

About Pituitary Adenoma
Pituitary adenoma is a benign tumor that arises from the pituitary gland, a small gland located at the base of the brain. This gland is crucial for regulating various hormones that control important bodily functions, including growth, metabolism, and stress responses. While pituitary adenomas are generally non-cancerous, they can lead to significant health issues depending on their size and the hormones they affect.
Causes of Pituitary Adenoma
The exact cause of pituitary adenomas remains unclear. However, several factors may contribute to their development, including:
- Genetic Factors: Certain genetic syndromes, such as Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN) type 1, increase the risk of developing pituitary adenomas.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Disruptions in hormone levels may play a role in the growth of these tumors.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to radiation and other environmental influences may also be potential risk factors.
Types of Pituitary Adenoma
Pituitary adenomas can be categorized based on their size and hormonal activity:
- Microadenomas: Tumors smaller than 1 centimeter, often asymptomatic but can cause hormonal imbalances.
- Macroadenomas: Larger than 1 centimeter and can lead to more pronounced symptoms due to pressure on surrounding structures.
- Functioning Adenomas: These tumors produce hormones, leading to conditions like acromegaly (growth hormone excess), Cushing’s disease (excess cortisol), and prolactinomas (excess prolactin).
- Non-Functioning Adenomas: These do not produce active hormones but may still cause symptoms due to their size and pressure effects.
Symptoms of Pituitary Adenoma
Symptoms of pituitary adenomas can vary based on the type and size of the tumor. Common symptoms include:
- Headaches: Persistent headaches that do not respond to typical pain relief methods.
- Vision Problems: Blurred or double vision, or peripheral vision loss due to pressure on the optic nerves.
- Hormonal Changes: Symptoms like unexplained weight gain, changes in libido, menstrual irregularities, or excessive sweating.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Resulting from increased intracranial pressure.
Diagnosis of Pituitary Adenoma
Diagnosing a pituitary adenoma involves a comprehensive evaluation, including:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: A detailed assessment of symptoms and medical background.
- Imaging Tests: MRI and CT scans are essential for visualizing the tumor and determining its size and location.
- Hormonal Testing: Blood and urine tests to evaluate hormone levels and identify hormonal imbalances.
Treatment for Pituitary Adenoma
Treatment options for pituitary adenoma depend on the type and size of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health:
- Monitoring: Small, non-functioning tumors may only require regular monitoring.
- Medications: Hormonal medications can effectively treat certain functioning adenomas.
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor is often necessary for larger tumors or those causing significant symptoms. Dr. Sandeep Vaishya specializes in minimally invasive techniques to reduce recovery time and risks.
- Radiation Therapy: This may be used post-surgery or for tumors that cannot be completely removed.
Cost of Treatment and Stay in India
The cost of treatment for pituitary adenoma in India can vary significantly based on factors like the complexity of the case, hospital choice, and the type of treatment required. Generally, the approximate costs are as follows:
- Initial Consultation: $50 – $150
- Imaging Tests (MRI/CT): $100 – $500
- Surgery: $3,000 – $8,000
- Post-operative Care: $500 – $1,500